The nature of the process manufacturing industry is characterised by high capital investments, most of which is for the machines & equipment employed in production. In order to ensure that your business obtains maximum return on this crucial investment it is absolutely essential to ensure that these equipment & machines perform to the best of their potential and are always maintained in their most optimal performing state. In this context plant maintenance activities assume huge importance and are inevitable for an efficient production system. Maintenance activities are very crucial for a wide range of reasons.
Clearly, increasing power consumption uses more fuel.
Optimal maintenance strategy aims to increase of MTBF (Mean Time between Failures) and reduction of MTTR (Mean Time to Repair) in all areas. This directly impacts the operating cost, profitability, customers’ demand satisfaction, and productivity among other important performance requirements.
The minimization of machine breakdowns and down time is the main objective of maintenance but the right plant maintenance strategy varies from one organization to another, basically depending on their nature of operations and the frequency of maintenance activities required.
Maintenance may be classified as:
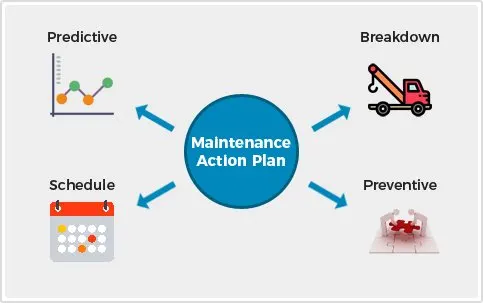
In this strategy maintenance activities in plant are carried out after the equipment is out of order and it cannot perform its normal function any longer, e.g., an electric motor breakdown, a conveyor belt complete wear out, etc. On deducting an issue the production department calls on the maintenance department to rectify the defect. The maintenance department checks into the difficulty and makes the necessary repairs. After removing the fault, maintenance engineers do not attend the equipment again until another failure or breakdown occurs. The major drawback of this being stoppages or delays in production, faster plant deterioration and as a result reduced or direct loss of profit.
This strategy of plant maintenance in manufacturing industry is employed with the objective to minimise the problem of breakdown maintenance. Maintenance activity is carried out before the failure arises or prior to the equipment actual breakdown. It is a safety measure designed to minimise the possibility of unanticipated breakdowns and interruptions in production. This ensures Reduction of total downtime, reduction in production losses, and increased equipment life. Periodic Equipment Calibration is one important Preventive maintenance activity.
Equipment Calibration
Equipment calibration is an important activity performed when a new instrument is initially installed and commissioned. Calibration verification and any necessary adjustments are completed to ensure operation is within specification. Annual Calibration and Preventive Maintenance guarantees that the instrument continues to operate to specification while minimizing the risk of unexpected failures. Industry standards specify that Scheduled onsite Calibration and Preventive Maintenance services are required every year to prolong the life of the instrument by reducing the potential for a minor issue becoming a major problem.
The main problem in preventive maintenance is to decide accurately when equipment should receive attention.
This includes all work undertaken to keep the production equipment in efficient condition. It may cover periodic inspection, cleaning, lubrication, overhaul, repair, replacement, etc. These operations are performed either while the equipment is running or during pre-planned shutdowns. It aims at avoiding breakdowns or minimizing it as far as possible. The main advantages being reduced risk factor, as the equipment and building are being regularly checked decreasing the risk to breaking down without notice, money saving as lesser equipment/tools will have to replaced, lesser energy wastage as equipment will be in optimal operating condition, and reduced disruptions in production. However Scheduled maintenance could result in over maintenance, as equipment might be serviced more than required resulting in expending more money and manpower.
In this approach maintenance activities are carried out on the prediction of any fault. For example, unusual sounds coming out of rotating equipment predict a coming trouble, or an electric cable excessively hot at one point predicts a trouble. In this strategy periodic measurement of the equipment’s conditions happens and this enables timely action such as equipment adjustments, repair or overhaul. In this strategy of plant maintenance in manufacturing industry maintenance tasks are planned based on the actual condition of the equipment rather than on some predetermined schedule. Predictive maintenance extends the service life of equipment without fear of failure. However this method Increases investment in diagnostic equipment and staff training
Machine breakdown is a nightmare for any manufacturing organization. When a vital production involving equipment fails it results in production stoppage and the losses would be huge.
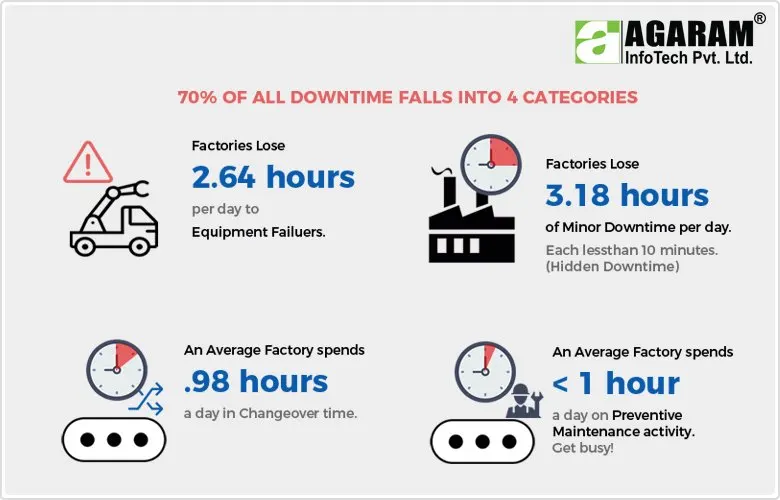
In this context the selection of the right maintenance strategy for your plant assumes great significance. Every equipment in your plant will need a different mix of the earlier specified maintenance activities. Devising the right plant maintenance strategy can be achieved if the two basics criteria of plant maintenance are acknowledged
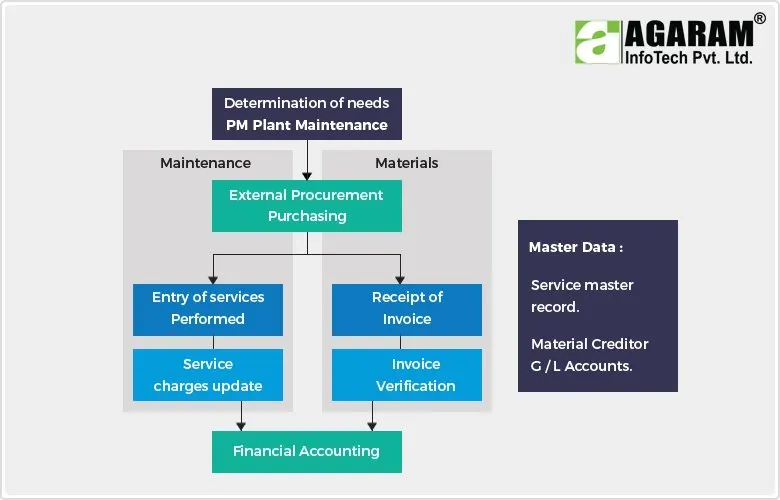
Process manufacturing plants typically run continuously, 24x7. Ensuring Optimal Production of quality items with available resources producing maximum business profit requires that companies embark on internal methodologies to design out flaws in their plants on an ongoing basis. In order to achieve this goal a manufacturing company requires a comprehensive Manufacturing Solution that which offers valid equipment data diagnostics and ensures inter-organisational communication and collaboration. The solution should be accessible to the procurement, inventory, operations, technical, safety and maintenance teams in the organization and facilitate the flow of business data through various departments to ensure the capture and processing of equipment information to ensure the application of the right Plant maintenance strategy at the right time.